
NVIDIA first became popular in 1996 for its chip on the Diamond 3D Edge accelerators, and later with its work on Sega projects. But it was the release of Riva 128 on the 3rd quarter of 1997 that NVIDIA really hit the markets. Riva was followed by TNT/TNT2 series but the real innovation over all was the embedding of T&L (Transform&Lighting) unit in the GeForce256 series in 1999.
GeForce256 was again followed by better models like GeForce2GTS/Ultra but we had to wait to see a brand new product until the 27th of February, 2001. It was then the GeForce 3 series was released. After a year, on the 6th of February NVIDIA has announced their new GPU, called GeForce4 and the graphic cards using this new core had flooded the market.
GF4, with the project name NV25, has in fact took start with the X BOX. It has too many common points when compared to the NV2A core which is used in XBOX.
GeForce 4 Titanium(NV25) series is made up of two models which are called GeForce 4 Ti 4600 and GeForce4 Ti 4400. But the rumor says that a third model named Ti 4200 with lower core and RAM frequencies will be released with in 3-5 weeks.
| Ti4600 | Ti4400 | Ti4200 | |
| Chip Clock | 300 MHz | 275 MHz | 225 MHz |
| Memory Clock | 650 MHz (DDR) | 550 MHz (DDR) | 500 MHz (DDR) |
| Amount of Memory | 128 MB | 128 MB | 128 MB |
| Memory Bandwidth | 10,400 MB/s | 8,800 MB/s | 8,000 MB/s |
NV25 is manufactured with 0.15 micron production technology and consists of 63 million transistors. This means it has only 3 million more transistors than GF3 (NV20). NV25 has nFiniteFX-II, Accuview Antialiasing, LightSpeed Memory Architecture II and nView. Besides from NV17, NV25 does not have a VPE (Video Processing Engine), however has dual vertex shader and far ahead with 4 rendering pipelines. New generation T&L unit with faster frequency can render 100Million vertices per second.
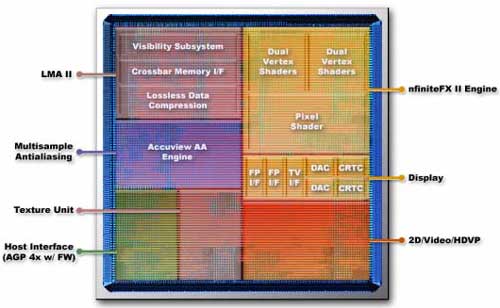
nFiniteFX-II
The most important thing about NV25 is nFiniteFX-II. nFiniteFX unit has the pixel and vertex shaders but unlike GeForce3, GF4 has two vertex shaders and thus it is called nFiniteFX-II. Moreover, it has better DirectX 8 integration and supports Pixel Shader v1.3. Thanks to the Dual vertex shader and the T&L unit which can draw 100Million vertices per second, it can render complex scenes (the picture below is taken from one of NVIDIA’s product demos, Werewolf) much faster. This demo performs 97,000 polygons per frame, 61 bones (6 bones/vertex) and 8 blended fur layers. Real time Per-Pixel lighting (Vertex Shader) and Matrix Palette Skinning (Vertex Shader) combined with independent shadow mapping makes this demo a real GF4 show-off. After all it only works with GF4 series and helps us to get a feeling about the future plans of NVIDIA. (If you already have a GF4 you can download the Werewolf demo from here)

LightSpeed Memory Architecture II
In the previous GeForce3 series (NV20), NVIDIA has used LightSpeed Memory architecture to get rid of the bottleneck effect of RAM bandwidth. This architecture is now upgraded to version II and is build up of the following 6 segments. These parts were already in NV20 but now they are improved.
Crossbar Memory Controller
LMA-II again uses the Crossbar architecture but now NV17 uses 2 memory controllers (NV25 has 4) These independent memory controllers access the RAM with smaller bits instead of 128bit (256bit chunk) blocks. For instance, to read the 32bit color + 32bit Z-buffer data, memory controllers access the memory with 64 bit, instead of 128 bit. This leaves 50% of the bandwidth unused.
Quad Cache
LMA-II also has a caching subsystem. It caches the primitive, vertex, texture and pixel data and sends them to NV17 without any access to the main memory. Quadcache can proves to be worthy especially in the rendering of complex scenes using for instance tri-linear filtering. However there is not a trustable acknowledgement about the size of this cache.
Lossless Z Compression
Storing the depth data of 3D scenes, Z buffer data can reach great values at 60 fps in high resolution. NVIDIA compresses this data at a rate of 1:4 in real time and thus reduces the bandwidth allocation to 1:4.
Z-Occlusion Culling
The conventional graphics architectures processes all the pixels and triangles in a 3D scene. So that even the data that won’t be seen in the scene is also processed. What Z-Occlusion Culling does is to eliminate this needless data. As a result the GPU and bandwidth is reclaimed and used for other processes.
Auto Pre-Charge
To understand Auto Pre-Charge, one needs to have some knowledge about the architecture and the operation logic of DRAM’s (Dynamic Random Access Memory) Shortly, it is a system designed to reduce the time loss when the GPU tries to access an inactive bank of DRAM.
Fast Z-Clear
We previously stated that Z-buffer data occupied huge amount space and was used for storing the 3D depth. The faster you transfer and the more you compress this data, the more free bandwidth you will have. Also clearing the old data and writing over should be fast for better performance. GF4 quickly gets rid of the old data by replacing it with “0”. However this is not a new technique. ATI radeon was using it before.
Accuview Antialiasing
GeForce 3 came with a new FSAA antialiasing method called “Quincunx” which was faster and better than 2X AA. GeForce 4 introduces a new antialiasing method called “Accuview” with the logic figured out below.
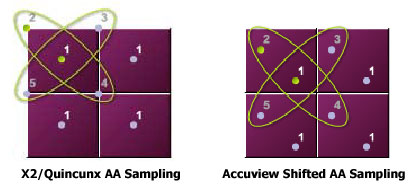
Accuview is in fact using the same logic with Quincunx, but this time the pixels are shifted. So that more data is gathered from the near by pixels to render a better positioned and antialiased pixel. The result is an improved image quality. Since GF4 has a dedicated unit for this process, it works very quickly. GF4 also has another antialiasing method called 4xS. This method can only be used with Direct3D and can perform better than 4x antialiasing.
nView
NV17 has two 350 MHz. RAMDACs and TDMS for Flat Panels. You can connect multiple monitors to your graphic card. Although NVIDIA supported dual-screen since GeForce2 MX series, none of them was utile like Matrox GXXX series. The only reason was the lack of effective software. nView is removing this drawback and makes it easier to work with multiple screens. By the way this utility is not bound to the hardware. Any detonator driver with this software will enable you to use multiple desktops just like the Linux 🙂
Ok, now back to Asus V8460Ultra; The one in the picture below is the top model of the series. It has 300 MHz. core and 650 MHz. (325 MHz. DDR) frequencies. The total memory is 128 MB and operates at 2.8 ns. Unlike the ones on the previous graphic cards, these RAMs are surface-mount. They have the potential to work at 714 MHz. (1000/2.8=375 MHz. DDR). With these RAMs, V8460Ultra can offer a bandwidth of 10400MB/s

The “Ultra” at the end of v8460 Ultra is because of NV25. This chip works at 300MHz. The one that we used for comparison test, Asus v8440 does not have such a name convention. The heatsink and the fan are very close to the reference design of NVIDIA and enough for cooling the NV25 GPU. RAM heatsinks, which we frequently saw on 250 MHz Rams of GF3s, does not exist on 325 MHz. DDR’s of GeForce 4.

Besides 15Pin D-Sub standard monitor output, V8460 Ultra also has a DVI output. Using the adaptor that comes with the product you can use this output to connect to another standard monitor to benefit dual-screen feature. Moreover, with the Conexant CX25871-14 video encoder, it offers fine quality S-Video and Composite video outputs. This model that we test here is called V8460Ultra/TD. There are also two more versions of this card. One is V8460/DVI, which lacks VideoOut and the other is as usual, V8460Ultra/Deluxe. The deluxe model has Video I/O and 3D Glasses. Another change in the design is the PCB color. In addition to the color (that you see on the above picture), there are also PCB’s with purple color. Of course you don’t care about the color like me, there is no problem 🙂

Full versions of Aquanox and Midnight GT games, Drivers CDs, Asus DVD2000 soft DVD Player and a Game Showcase including Comanche 4, Operation FlashPoint, Delta Force, Collin McRae 2.0, Incoming Forces and Rally Championship Extreme are also bundled with the product.
Now let’s look at the performance results of Asus V8460Ultra. We have used the below system as test setup. All tests are performed at 60 Hz. with VSYNC OFF on WinXP OS.
| Test Setup | |
| CPU | Athlon XP2000 |
| Memory | 256MB PC2700 CAS2 DDRRAM |
| Motherboard | Asus A7V333 |
| Video Card | Asus V8460Ultra 128MB (300/325MHz) Asus V8440 128MB (275/275MHz) ABIT Suliro GF3 64MB (200/230MHz) Asus V8170 64MB (270/200MHz) |
| Hard Drive | Seagate 330620 |
| Miscellaneous | Toshiba 32x CDROM, ElanVital 300W PSU 3Com 3C905B-TX ethernet |
| Software | Windows XP build 2600 NVIDIA DetonatorXP v28.32 Direct X 8.1 build 820 |
First of all, we will use the popular benchmark program for DX8, 3DMark2001 SE. You can see on the chart below that V8460Ultra and V8440 give close results. However the gap is huge between GeForce3 and V8460. At 1024x768x32 there is 39% and at 1600x1200x32 there is 51% performance difference. With some overclocking and using Win98SE, you can get a high ranking on MadOnion’s website with V8460Ultra.

In the high polygon test of 3DMark there is not much difference between V8460Ultra and V8440. And that little difference is because of the difference in RAM and Core freqencies. However, again it is much better that GeForce 3. With 1 light source, V8460Ultra is two times faster, and with 8 light sources it is far better. From these results we can conclude that new features like Z-Occlusion Culling and Fast Z-Clear really work. Even GeForce 4 MX440 beats GeForce 3 at high polygon tests, thanks to these new features.


